Automating Keyword Research: A Google Sheets Workflow for Marketers
Automating keyword research: a Google Sheets workflow that scales content ideas and briefs

Automating keyword research: a Google Sheets workflow that scales content ideas and briefs
The modern digital marketing team moves fast when keyword research is automated, repeatable, and tightly connected to content goals. A Google Sheets–driven workflow can serve as the central nervous system for collecting data from multiple sources, normalizing and deduplicating it, clustering topics, and generating ready-to-use content briefs. This article walks through a concrete, end-to-end workflow you can implement today—zeroing in on a modular, replicable setup that scales per domain while preserving editorial standards. It emphasizes governance, data hygiene, and measurable impact, so teams can compare automated keyword research outcomes with traditional methods and continuously improve how they ideate, plan, and publish.
Why keyword research automation is a game changer for digital marketers
The time sink of manual keyword discovery
In many organizations, keyword discovery is a manual, fragmented process: pull lists from a few tools, skim the SERP landscape, copy/paste ideas into a spreadsheet, then handcraft briefs. The time spent on data collection, deduplication, and sanity checks translates directly into fewer content topics and slower time-to-market. A well-designed automated workflow reduces repetitive steps, accelerates ideation, and returns hours previously spent on manual curation to the team. The gains compound as you scale to multiple topics, languages, or regions.
Automation also reduces variability across campaigns. When the same rules apply to every dataset, results become more predictable. Consistency matters for coverage, topic relevance, and alignment with business goals. In short, automation helps content teams produce more in less time, enabling faster response to market signals and seasonal trends.
Aligning automation with content goals and ROI
Automation should be tethered to measurable outcomes: broader topic surface area, higher relevance to business goals, faster brief generation, and improved content velocity. The ROI isn’t only about saving hours; it’s about increasing the quantity and quality of content you can publish in a given period without sacrificing editorial standards. A well-governed, automated keyword research workflow makes it easier to map each keyword to a business objective (informational, comparison, transactional) and to defend editorial decisions with data. When the workflow surfaces “your keyword” topics that tie directly to core offerings or high-intent products, the ROI becomes tangible in engagement, conversions, and downstream ranking signals.
Designing a repeatable automated keyword research workflow
Define your data sources and inputs
A practical automated workflow begins with explicit input sources and a consistent data schema. Typical sources include:
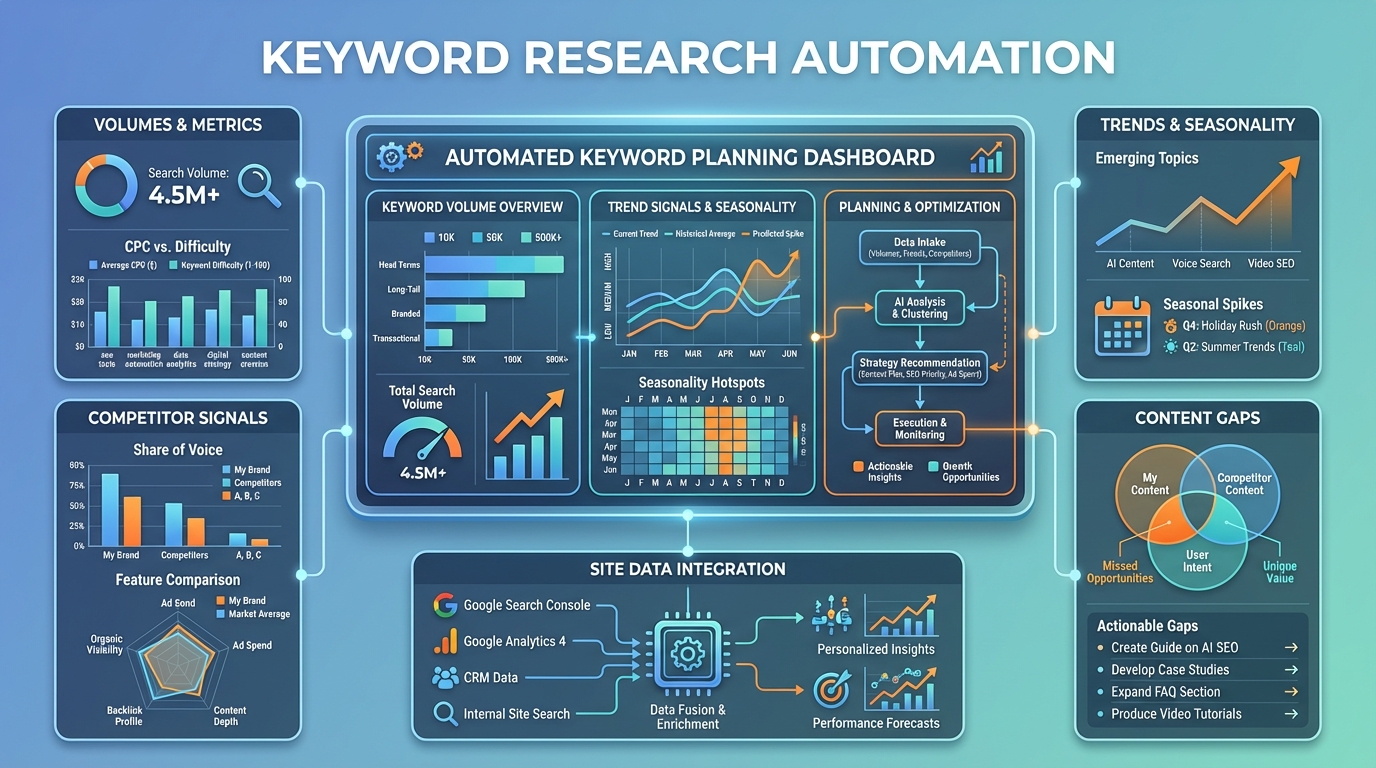
- Keyword planners and keyword databases (e.g., Google Ads Keyword Planner or alternatives that expose volumes, trends, and difficulty signals)
- Trends and seasonality signals (Google Trends, other trend services)
- Competitor signals (keywords that appear on competitor pages, ranking pages, or content gaps you can fill)
- Site data (internal site search query logs, top landing pages, historically successful topics)
- SERP features and intent signals (question-based queries, comparison terms, product-specific searches)
- Content performance data (historical traffic, engagement metrics, and ranking trajectories for existing posts)
Each source should feed into a structured input tab (for example, a RawKeywords tab) with fields like:
- Keyword text
- Source name
- Volume or search interest
- Difficulty or competitiveness signal
- Intent assumption (informational, navigational, transactional)
- Date last updated
- Confidence score (optional)
Data quality is essential here: prefer clean, reputable sources, note data caveats, and track update cadence. Seasonality should be captured by historical volumes or trend data so that you don’t overreact to short-term spikes.
Google Sheets as the central hub for automation
Google Sheets works best as the central hub because it’s collaborative, scriptable, and integrates with data sources via simple imports or custom APIs. A robust Google Sheets setup uses a multi-tab architecture to separate concerns while enabling clear data lineage. A practical structure might include:
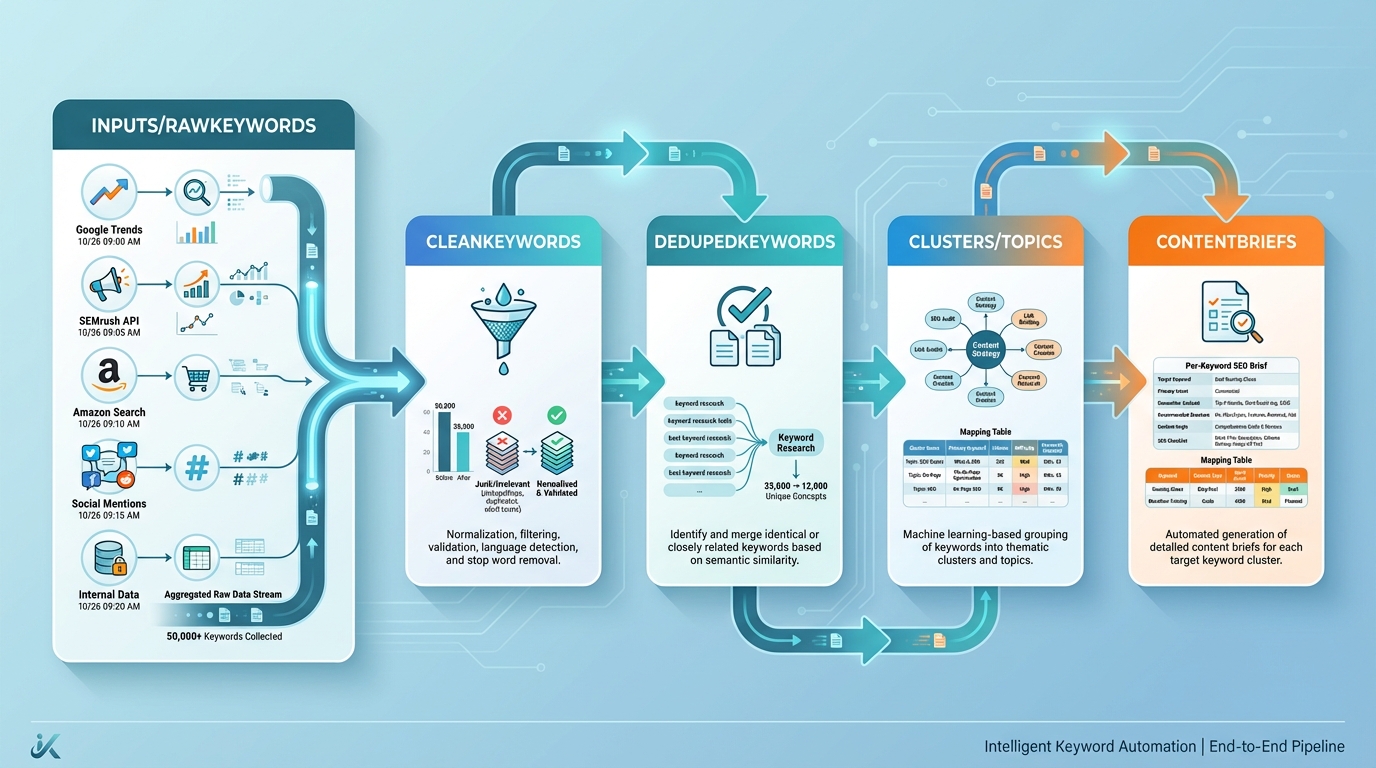
- Inputs or RawKeywords: copies from all data sources; includes source identifiers and timestamps
- CleanKeywords: normalization and basic cleaning (lowercasing, punctuation removal)
- DedupedKeywords: deduplicated keyword list across sources
- Clusters or Topics: keyword-to-topic mappings based on simple heuristics or a mapping table
- ContentBriefs: per-keyword briefs with topic, angle, and SEO guidance
- Scoring or Signals: calculated metrics (volume, relevance, difficulty, seasonality)
- Dashboards: visualizations of coverage, topic breadth, and velocity
- Settings: automation rules, API keys, and update schedules
Key formulas and patterns you’ll reuse:
- Normalization and cleaning
- Lowercasing and cleanup: =LOWER(TRIM(REGEXREPLACE(A2, "[^a-z0-9\s]", "")))
- Deduplication
- Unique keywords:
=UNIQUE(FILTER(CleanKeywords!A:A, CleanKeywords!A:A<>""))
- Unique keywords:
- Basic topic mapping (simple cluster hook)
- If you maintain a TopicMapping table, you can map a keyword to a topic with VLOOKUP: =IFERROR(VLOOKUP(LEFT(CleanKeywords!A2, FIND(" ", CleanKeywords!A2&" ")-1), TopicMapping!A:B, 2, FALSE), "Misc")
- Scoring
- A simple composite score combining volume and relevance (illustrative) =IFERROR(Volume!B2 * Relevance!C2, 0)
- Data refresh hooks
- Use IMPORTXML/IMPORTDATA/IMPORTHTML for lightweight sources where allowed, or Apps Script to call APIs and write results into RawKeywords.
The goal is a clean handoff: sources → normalization → deduplication → topic mapping → briefs, with a time-stamped record of updates to support governance.
Turning keyword data into actionable content topics
With a clean keyword set in place, the next step is to translate data into actionable content topics. A practical approach uses clustering by topics and intent to generate briefs aligned with editorial goals.
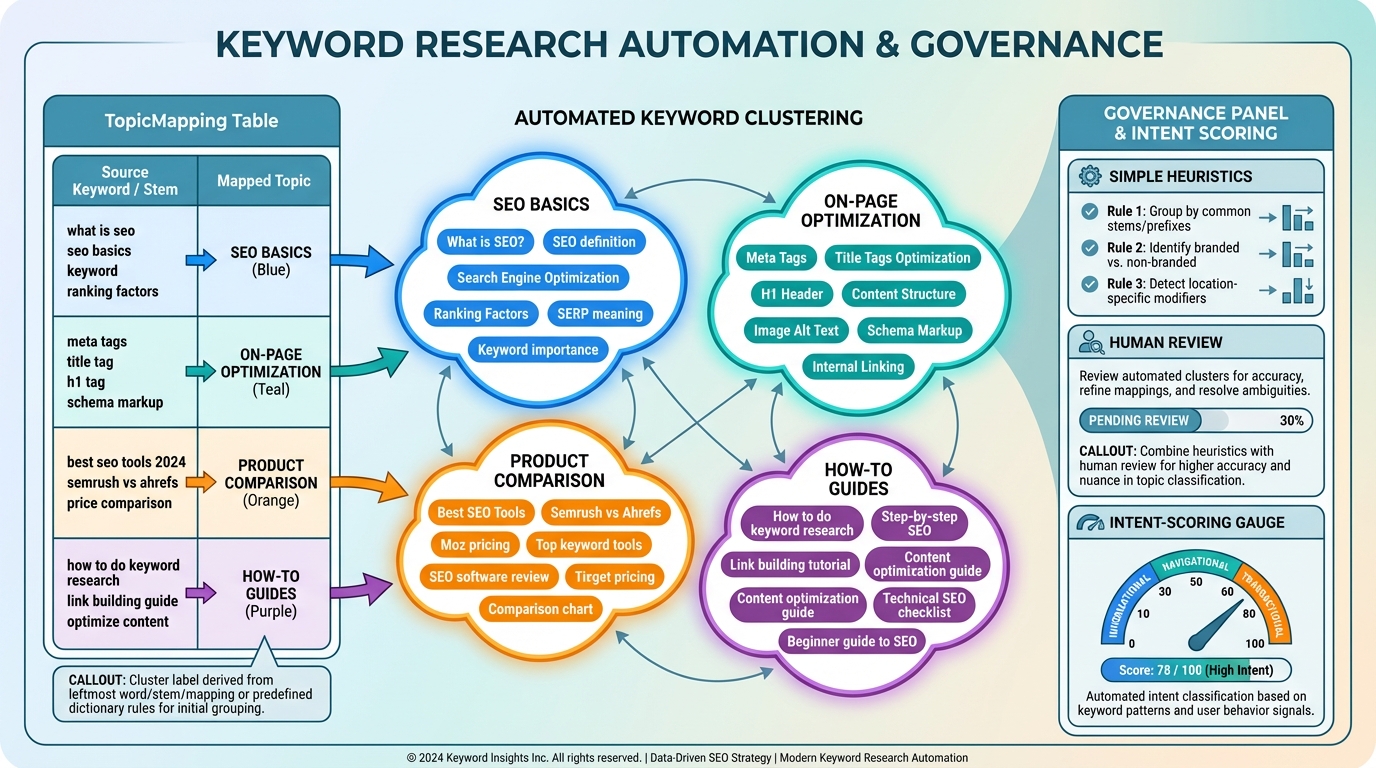
- Clustering basics
- Use a TopicMapping table (or an algorithmic approach) to assign keywords to topics such as “SEO basics,” “on-page optimization,” “product comparison,” or “how-to guides.”
- The cluster label can be derived from the leftmost word, a stem, or a predefined mapping. For higher accuracy, combine simple heuristics with human review in the governance stage.
- Intent alignment and scoring
- Attach an intent tag (informational, navigational, transactional) to each keyword. Combine this with volume and difficulty to prioritize topics that both align with goals and have strong potential impact.
- From keywords to content briefs
- For each keyword, generate a structured brief with: target keyword, suggested title, intent, audience, core angle, suggested headings, and on-page guidance (density, key term usage, related terms).
- The brief should also include a suggested internal linking plan and a call to action aligned with the business objective (e.g., product page, trial signup, or resource download).
A simple “ContentBrief” row might contain:
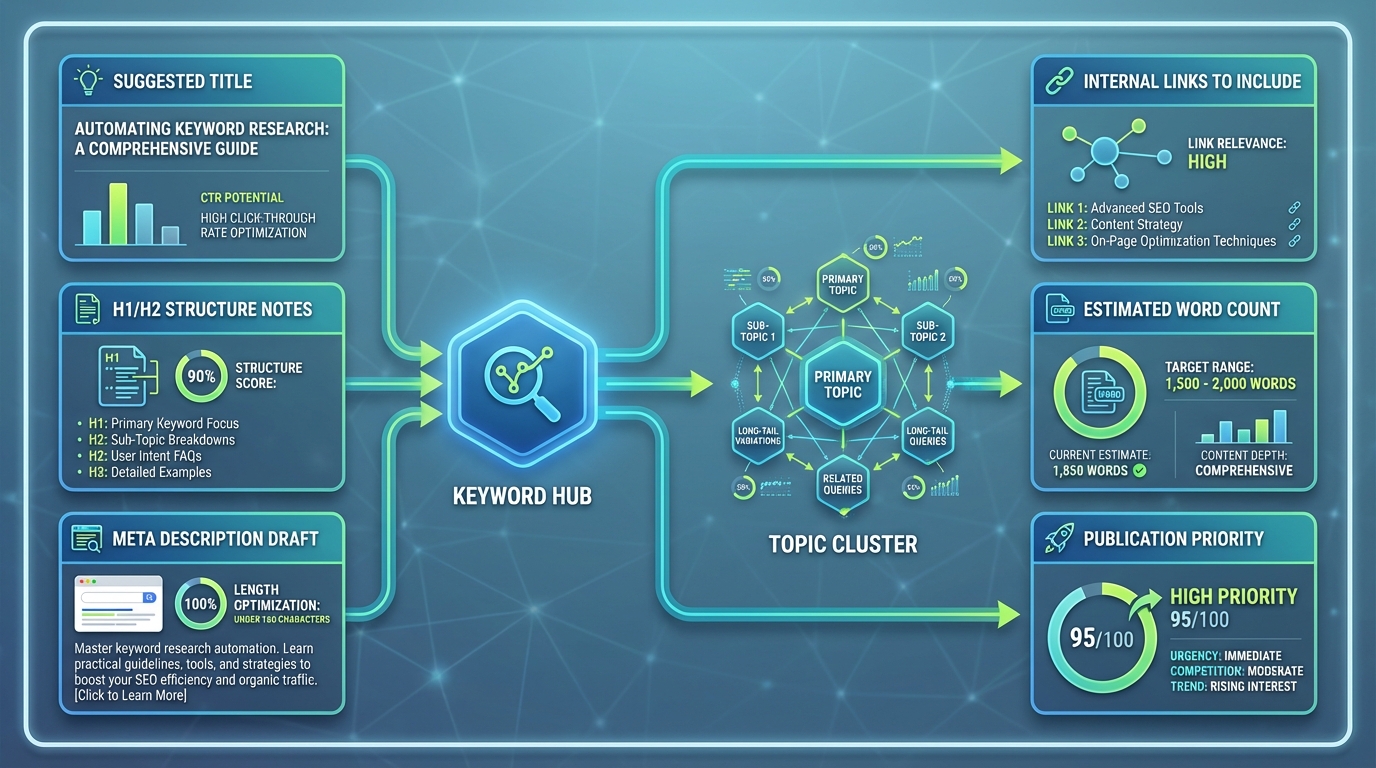
- Keyword
- Topic cluster
- Target keyword usage guidelines
- Suggested title
- H1/H2 structure notes
- Meta description draft
- Internal links to include
- Estimated word count
- Publication priority
This is where automation shines: a single row per keyword, populated automatically with a ready-to-edit draft, ready for a content creator to review or refine in a single pass.
Practical templates and patterns you can reuse
A reusable Google Sheets workflow: structure, formulas, and triggers
A practical template emphasizes modularity and governance. Here’s a lightweight blueprint you can adapt:
-
Tabs and their purpose
- RawKeywords: push in data from all sources (with a Source field)
- CleanKeywords: normalized keywords
- DedupedKeywords: unique keywords
- Clusters: keyword → topic mapping
- ContentBriefs: one row per keyword with a ready-to-edit brief
- Scores: volume, difficulty, relevance, seasonality
- Dashboard: charts and metrics
- Settings: update cadence, APIs, and access controls
-
Example formulas and patterns
- Normalization: in CleanKeywords!A2 =LOWER(TRIM(REGEXREPLACE(RawKeywords!A2, "[^a-z0-9\s]", "")))
- Deduplication: DedupedKeywords!A2
=UNIQUE(FILTER(CleanKeywords!A:A, CleanKeywords!A:A<>"")) - Topic mapping (simple) In Clusters!B2 (for keyword in A2) =IFERROR(VLOOKUP(CleanKeywords!A2, TopicMapping!A:B, 2, FALSE), "Misc")
- Brief generation (conceptual)
In ContentBriefs!A2, pull keyword from DedupedKeywords and fill:
- Keyword: =DedupedKeywords!A2
- Topic: =Clusters!B2 (mapped)
- Title: =CONCAT("How to ", DedupedKeywords!A2)
- Brief: "Outline: Introduction to ", DedupedKeywords!A2, " ..."
-
Triggers and automation
- Apps Script can be used to schedule data pulls (daily or weekly), refresh imports, and push updates to the cluster and briefs.
- If you rely on lightweight imports (IMPORTXML, IMPORTHTML, IMPORTDATA), you can configure the data refresh behavior and store a timestamp in Settings.
-
Lightweight guardrails
- Enforce a minimum data quality threshold before a keyword moves from RawKeywords to DedupedKeywords (e.g., at least two sources, non-empty volume, and a confidence score above a threshold).
- Include a Status column in ContentBriefs (Draft, Under Review, Approved) to ensure editorial checks occur before publishing.
Automating keyword research end-to-end: tools and integrations
A practical end-to-end flow can be implemented with a combination of data sources, Sheets, and lightweight automation:
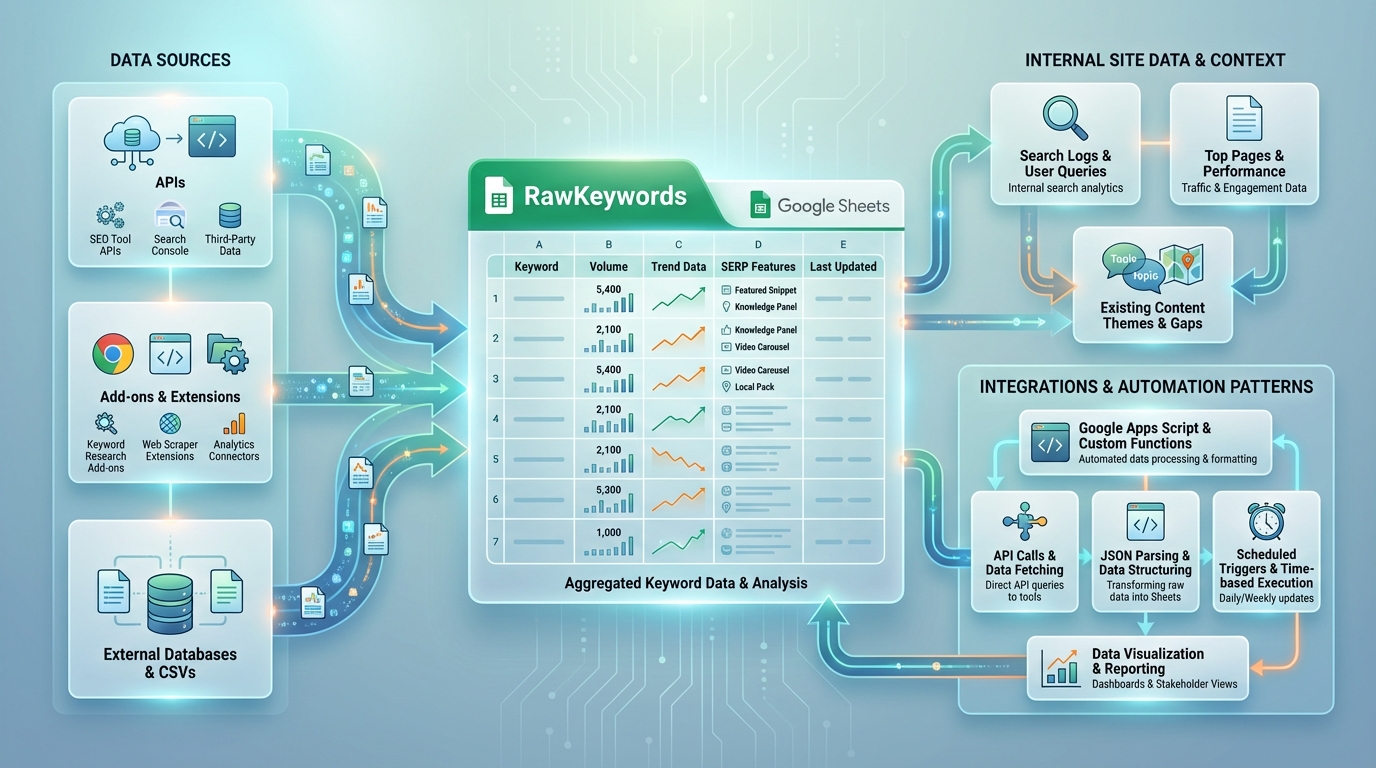
- Data sources to Sheets
- Use API connections or add-ons to fetch volumes, trend data, and SERP features into RawKeywords.
- Employ simple scripts or Add-ons to pull in site data (internal search logs, top pages) and align with existing content themes.
- Integrations and automation patterns
- Google Apps Script: write custom functions to call APIs, parse JSON, and populate RawKeywords; trigger on a schedule or when a sheet is edited.
- Zapier-like automation: connect data sources to Sheets so new keywords automatically flow into the workflow without manual import.
- Lightweight scrapers: for sources that don’t offer APIs, small scrapers (with caution for terms of service) can feed non-sensitive data into a dedicated RawKeywords tab, with proper governance and review.
- Data hygiene and governance
- Implement a stamping system: each keyword row includes a LastUpdated timestamp and a SourceTracker, so changes are auditable.
- Deduplication and normalization happen in dedicated tabs, ensuring downstream briefs rely on clean data.
- Role-based access and versioning controls protect editorial standards; automated outputs should follow a human-in-the-loop process for final approval.
Data hygiene, deduplication, and governance
Guardrails are essential to prevent low-quality output from driving decisions. Practical guardrails include:
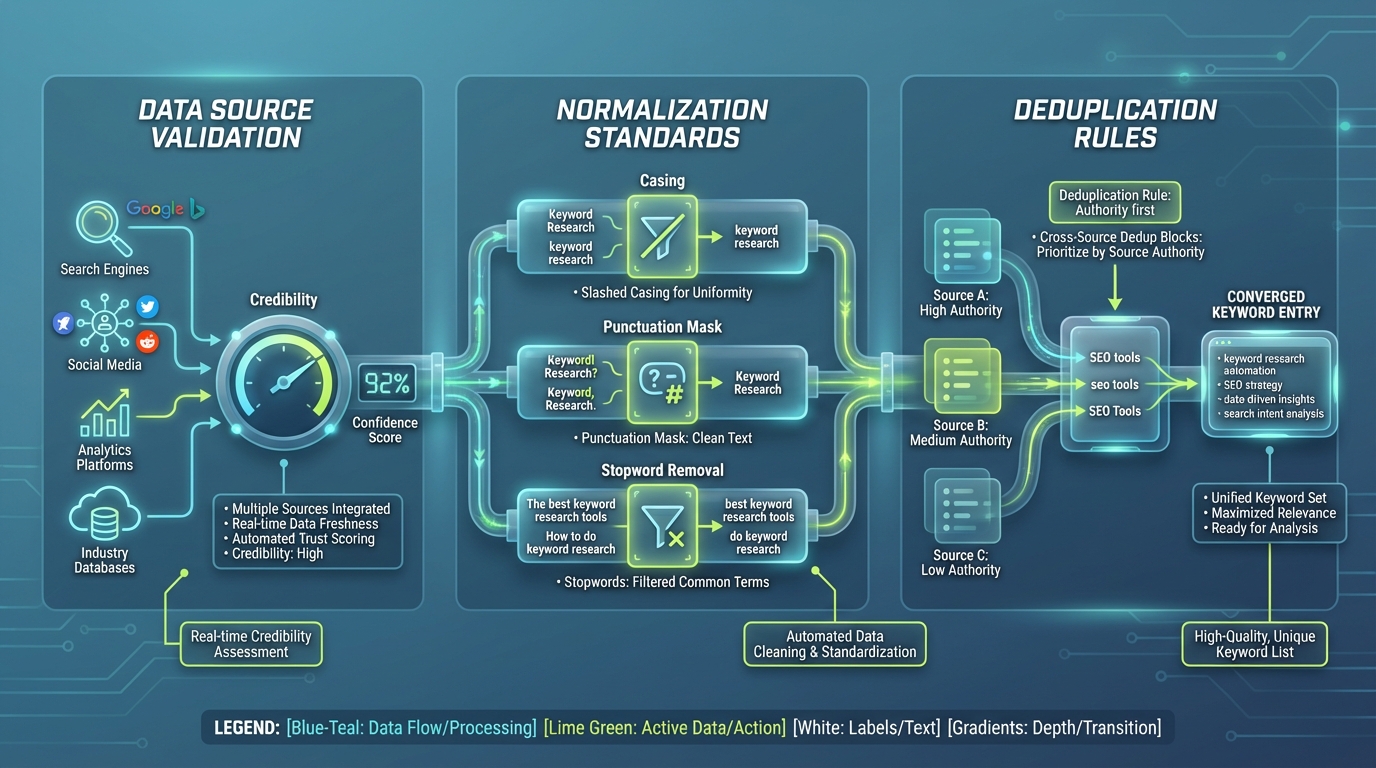
- Data source validation: require multiple sources for new keywords, or assign a confidence score based on source credibility and data freshness.
- Normalization standards: enforce consistent casing, punctuation handling, and stopword removal so that similar phrases converge into a single keyword entry.
- Deduplication rules: implement cross-source deduplication with a clear rule for authority (e.g., prefer the source with the highest volume or the most recent data).
- Seasonality handling: capture historical trends and weight seasonality so that topics don’t spike due to short-term events. Include a seasonality factor in the scoring model.
- Editorial guardrails: define a human-in-the-loop stage for high-visibility or high-risk topics (e.g., topics tied to product launches or sensitive markets). Use a status field and reviewer assignments to enforce checks before briefs move to publication.
- Version control: maintain a changelog, track updates to keyword lists, and store prior brief versions to support rollback if needed.
Measuring impact and scaling with confidence
Key metrics and dashboards for automated keyword research
A data-driven set of metrics helps you quantify the value of automation and identify opportunities to improve. Consider the following KPIs:
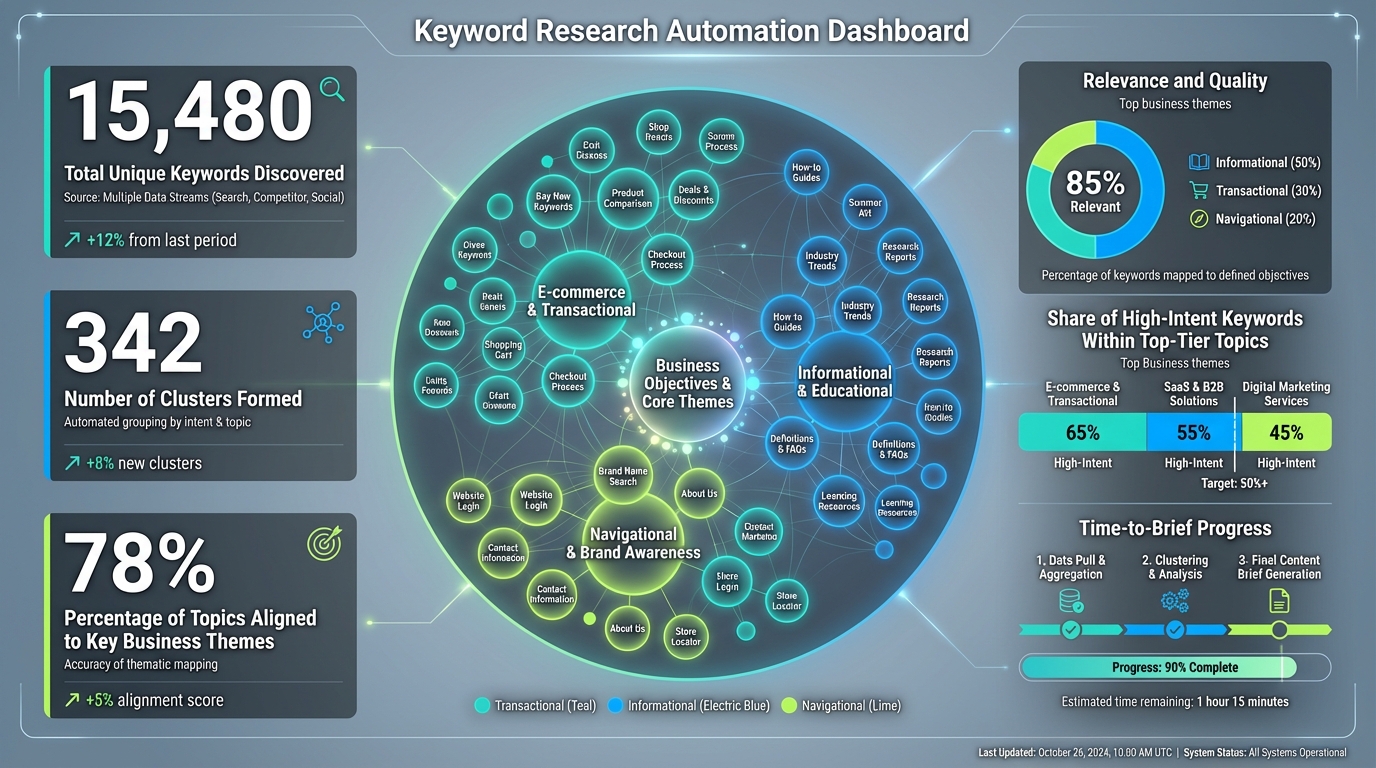
- Coverage and surface area
- Total unique keywords discovered
- Number of clusters/topics formed
- Percentage of topics aligned to key business themes
- Relevance and quality
- Percentage of keywords mapped to a defined business objective (informational, transactional, navigational)
- Share of high-intent keywords within the top tier of topics
- Efficiency and velocity
- Time-to-brief (from data pull to final content brief ready for review)
- Content briefs generated per week/month
- Editorial review cycle time
- Data quality and governance
- Percentage of keywords with multi-source validation
- Number of changes tracked in the changelog
- Review pass rate (percent approved on first pass)
- Outcome-oriented metrics
- Content performance for topics generated from automation (traffic, engagement, conversions)
- Ranking improvements for pages built around automation-sourced topics
Dashboards in Google Sheets can visualize these KPIs with a few charts:
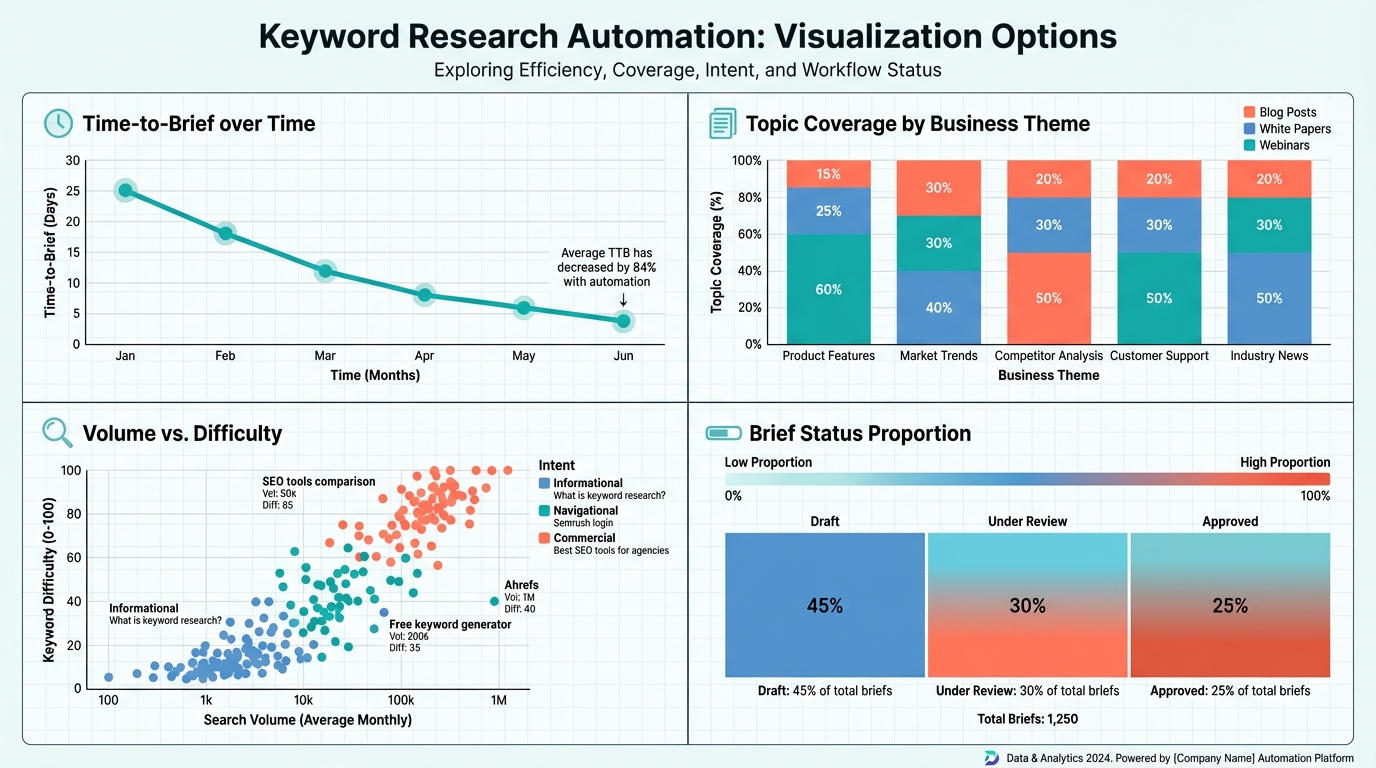
- A line chart for time-to-brief over time, illustrating efficiency gains
- A stacked bar chart for topic coverage by business theme
- A scatter plot of volume vs. difficulty with color by intent
- A status heatmap showing the proportion of briefs in Draft/Under Review/Approved
Governance and human-in-the-loop
Even the most sophisticated automated keyword research remains a collaboration between machine-driven insight and human judgment. A practical governance model includes:

- Clear review gates: automated results surface to a human editor for validation before briefs are finalized
- Editorial standards: a template for briefs aligned to SEO best practices, brand voice, and content strategy
- Role-based access: restrict critical changes to a subset of team members; audit trails for all edits
- Feedback loops: editors annotate changes and reasons for adjustments, which teaches the system and improves future clustering and scoring
- Change management: when sources or rules change, document adjustments and rerun historical data to maintain comparability
Real-world outcomes and future-proofing
A hypothetical but plausible case illustrates the impact. A mid-sized content team previously spent about 24–28 hours per week on keyword research, including data collection, deduplication, and initial briefs. After implementing a modular Google Sheets workflow with end-to-end automation, the team saw:
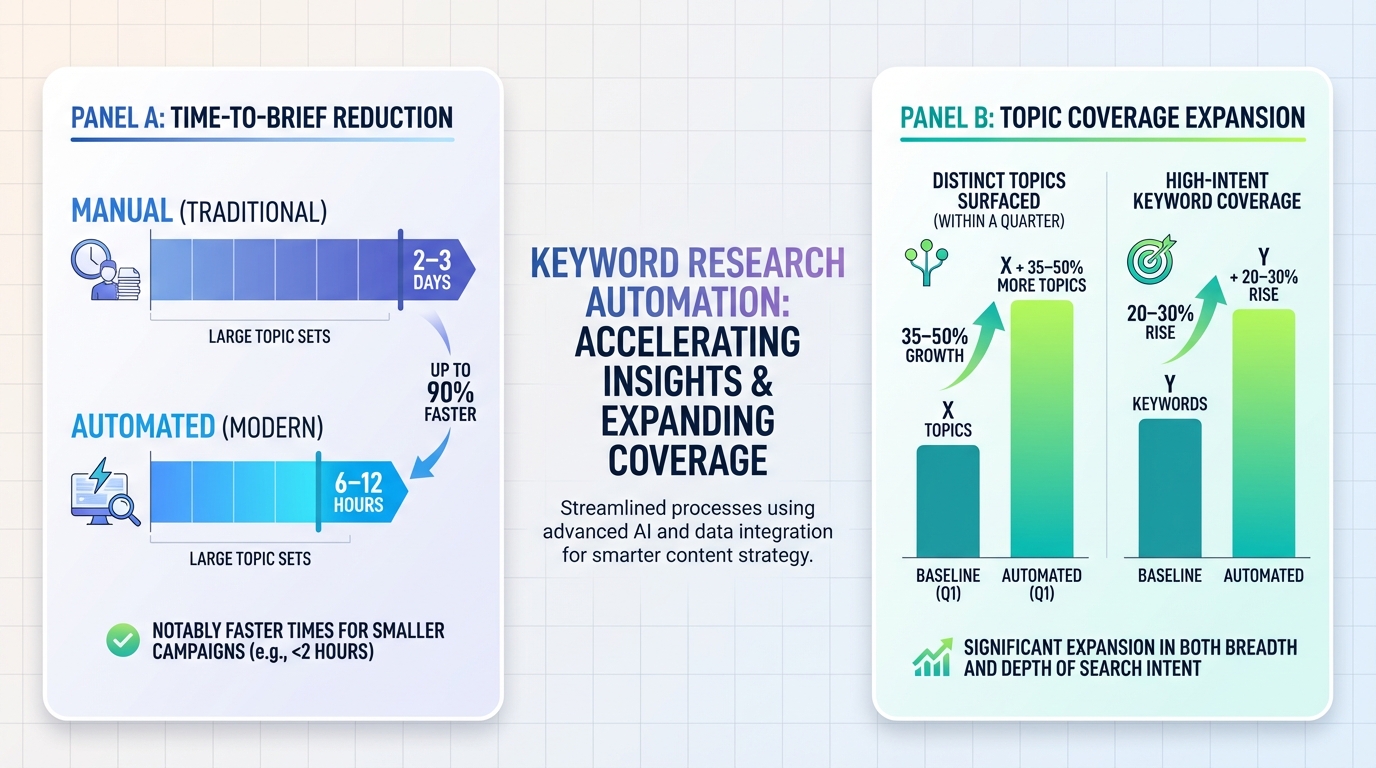
- Time-to-brief drop from 2–3 days to 6–12 hours for large topic sets, and even faster for smaller campaigns
- Topic coverage expansion: roughly 35–50% more distinct topics surfaced within a quarter, with a 20–30% increase in high-intent keyword coverage
- Content velocity improvements: the weekly volume of publishable briefs increased by 2–3x, enabling faster experimentation and cadence
- Editorial risk reduction: governance guardrails and human-in-the-loop checks reduced low-quality outputs by a meaningful margin, while maintaining editorial standards These outcomes are not hypothetical in a well-constructed workflow. They hinge on disciplined data inputs, robust deduplication, thoughtful topic clustering, and a governance layer that maintains editorial integrity while letting automation do the heavy lifting.
As teams mature, future-proofing comes from modularity and adaptability:
- Keep the Sheets architecture modular so you can swap or augment data sources without reworking the entire pipeline
- Use standardized data schemas and a shared vocabulary for topics and intents, so cross-domain replication remains accurate
- Plan for scale by pruning outdated topics and refreshing seasonal signals on a fixed cadence
- Codify best practices in templates so new domains can adopt the framework with minimal friction
Conclusion
Automating keyword research with a Google Sheets–centric workflow is not about replacing human judgment with machines; it’s about aligning data-driven insight with editorial discipline to accelerate content ideation and publishing at scale. By defining clear data sources, centralizing data in a single hub, and enforcing governance, teams can increase coverage, relevance, and velocity without sacrificing quality. The modular architecture—inputs, cleaning, clustering, briefs, and governance—lets you adapt the setup per domain while preserving a consistent standard of output. With practical templates, concrete formulas, and a disciplined human-in-the-loop, marketers can move from ad hoc keyword lists to a reliable, scalable engine for content strategy—where your keyword becomes a measurable driver of growth.
In a world where content velocity determines competitive advantage, this google sheets–driven approach offers a replicable blueprint: collect the right data, clean and deduplicate it, cluster into meaningful topics, generate actionable briefs, and govern every step with editorial checks. The result is a repeatable, scalable workflow for automated keyword research that supports smarter content plans, faster publishing, and stronger alignment with business goals.